🚀 SlimSAM(SAM压缩版,即“任意分割模型”)
SlimSAM是Segment Anything(SAM)模型的压缩(剪枝)版本,能够根据点或框等输入提示生成高质量的对象掩码。它通过创新的压缩方法,在大幅降低训练成本的同时,实现了接近原始模型的性能。
🚀 快速开始
提示掩码生成
from PIL import Image
import requests
from transformers import SamModel, SamProcessor
model = SamModel.from_pretrained("nielsr/slimsam-50-uniform")
processor = SamProcessor.from_pretrained("nielsr/slimsam-50-uniform")
img_url = "https://huggingface.co/ybelkada/segment-anything/resolve/main/assets/car.png"
raw_image = Image.open(requests.get(img_url, stream=True).raw).convert("RGB")
input_points = [[[450, 600]]]
inputs = processor(raw_image, input_points=input_points, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
outputs = model(**inputs)
masks = processor.image_processor.post_process_masks(outputs.pred_masks.cpu(), inputs["original_sizes"].cpu(), inputs["reshaped_input_sizes"].cpu())
scores = outputs.iou_scores
在生成掩码时,除了其他参数,你可以传入感兴趣对象的大致二维位置、包围感兴趣对象的边界框(格式应为边界框右上角和左下角的x、y坐标)、分割掩码。截至撰写本文时,根据官方仓库,官方模型不支持将文本作为输入。更多详细信息,请参考这个笔记本,它通过可视化示例展示了如何使用该模型!
自动掩码生成
该模型可用于以“零样本”方式根据输入图像生成分割掩码。模型会自动用一个包含1024个点的网格进行提示,并将这些点全部输入模型。
以下是自动掩码生成的示例代码:
from transformers import pipeline
generator = pipeline(task="mask-generation", model="nielsr/slimsam-50-uniform", device = 0, points_per_batch = 256)
image_url = "https://huggingface.co/ybelkada/segment-anything/resolve/main/assets/car.png"
outputs = generator(image_url, points_per_batch = 256)
以下是显示图像的代码:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
def show_mask(mask, ax, random_color=False):
if random_color:
color = np.concatenate([np.random.random(3), np.array([0.6])], axis=0)
else:
color = np.array([30 / 255, 144 / 255, 255 / 255, 0.6])
h, w = mask.shape[-2:]
mask_image = mask.reshape(h, w, 1) * color.reshape(1, 1, -1)
ax.imshow(mask_image)
plt.imshow(np.array(raw_image))
ax = plt.gca()
for mask in outputs["masks"]:
show_mask(mask, ax=ax, random_color=True)
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()
✨ 主要特性
SlimSAM是一种新颖的SAM压缩方法,通过统一的剪枝-蒸馏框架高效重用预训练的SAM,实现了卓越的性能和极低的训练成本。具体特性如下:
- 高效压缩:通过创新的交替瘦身策略,将压缩过程划分为渐进式步骤,在大幅减少参数和计算量的同时,保持接近原始模型的性能。
- 低训练成本:与其他现有方法相比,训练成本降低了10倍以上,仅需0.1%(10k)的SAM训练数据。
- 高性能表现:在参数数量减少至仅0.9%(570万)、MACs减少至0.8%(21G)的情况下,仍能实现接近原始SAM-H的性能。
📚 详细文档
模型详情
SAM模型由3个模块组成:
VisionEncoder:基于VIT的图像编码器。它使用注意力机制对图像块进行计算,以生成图像嵌入,并使用相对位置嵌入。PromptEncoder:为点和边界框生成嵌入。MaskDecoder:一种双向变压器,在图像嵌入和点嵌入之间进行交叉注意力计算,并将输出结果输入到Neck模块。Neck:根据MaskDecoder生成的上下文掩码预测输出掩码。
📄 许可证
本项目采用Apache-2.0许可证。
📜 引用
如果您使用此模型,请使用以下BibTeX条目进行引用:
@article{kirillov2023segany,
title={Segment Anything},
author={Kirillov, Alexander and Mintun, Eric and Ravi, Nikhila and Mao, Hanzi and Rolland, Chloe and Gustafson, Laura and Xiao, Tete and Whitehead, Spencer and Berg, Alexander C. and Lo, Wan-Yen and Doll{\'a}r, Piotr and Girshick, Ross},
journal={arXiv:2304.02643},
year={2023}
}
@misc{chen202301,
title={0.1% Data Makes Segment Anything Slim},
author={Zigeng Chen and Gongfan Fang and Xinyin Ma and Xinchao Wang},
year={2023},
eprint={2312.05284},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}
模型相关图片
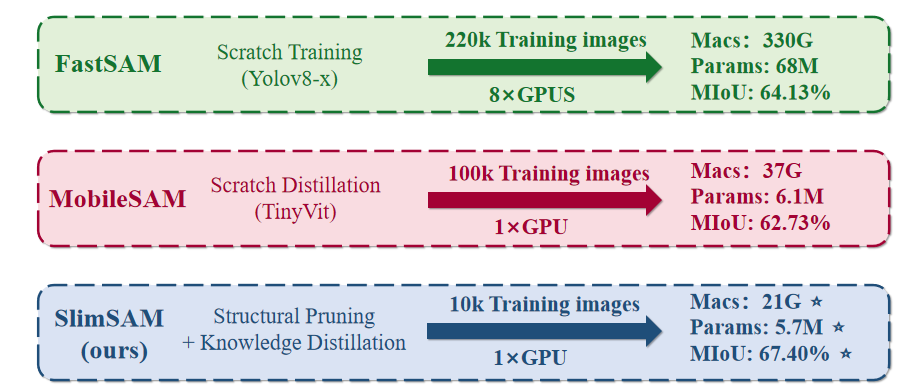 SlimSAM概述及其与其他替代方案的差异。
SlimSAM概述及其与其他替代方案的差异。
原仓库链接
点击查看原仓库
免责声明
本模型卡片的内容由Hugging Face团队撰写,部分内容从原始的SAM模型卡片复制粘贴而来。
 Transformers 支持多种语言
Transformers 支持多种语言 Transformers 支持多种语言
Transformers 支持多种语言 Transformers 英语
Transformers 英语 Transformers 英语
Transformers 英语 SlimSAM概述及其与其他替代方案的差异。
SlimSAM概述及其与其他替代方案的差异。